- What is district cooling?
-
District cooling is an advanced cooling system that reduces power peak load in summer by using alternative energy such as residual heat from a co-generation plant by supplying economically produced hot water or cold water to a certain area.
District cooling contributes to energy saving and environment improvement in our country.
- It improves the electricity shortage in summer due to cooling.
- Compared to other cooling systems with high electricity consumption, the electricity consumption is lower, which reduces the power load during summer.
- It protects the atmospheric ozone layer.
- It uses water as a refrigerant instead of greenhouse gas that causes global warming, such as Freon Gas (CFC); thus protecting the ozone layer and improving the atmospheric environment.
- It maximizes energy utilization.
- The cooling supply using district heating heat improves the utilization efficiency of the co-generation plant in summer.
Conceptual diagram of district cooling
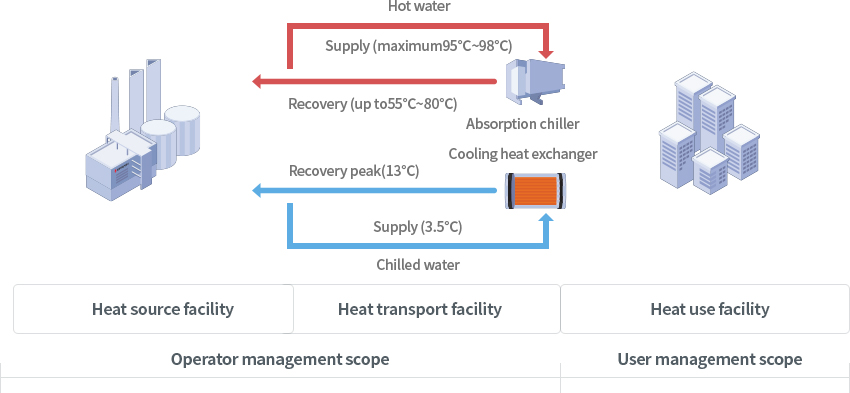
- Operator management scope
- Heat source facility
-
- Heat transport facility
- Absorption chiller : Hot water
- Supply (maximum 95℃ ~ 98℃)
- Recovery (up to 55°C ~ 80°C)
- Cooling heat exchanger : Cold water
- Supply (3.5℃)
- Recovery (peak ℃)
- User management scope
- Heat use facility
There are two main ways to provide district cooling.
- Cold Water Direct Supply Method
- Cold water is made from economical energy, such as residual heat produced by a co-generation plant and ice storage using late-night electricity, and is supplied directly to buildings through pipes in a large-scale built-up area.
- Hot Water Supply Method
- The residual heat generated by the generation of electricity from the co-generation plant is sent to the building's user facilities through pipes to make cold water using the absorption chiller and supply it to each room.
District Cooling Method
Hot Water Supply System
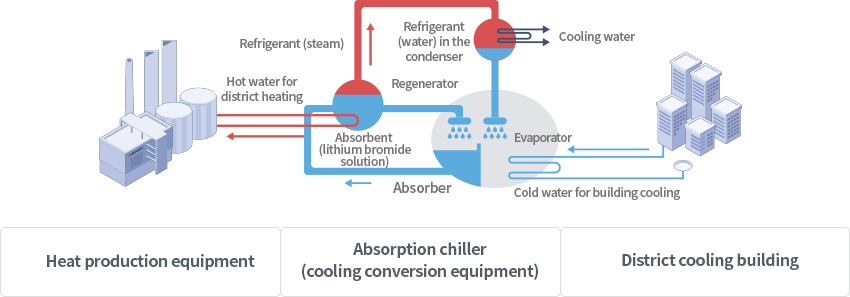
- Heat production equipment : Hot water for district heating
- Absorption chiller (cooling conversion equipment)
- Regenerator : Refrigerant (steam)
- condenser : Refrigerant (water) → Cooling water
- Evaporator
- District cooling building : Cold water for building cooling
- Absorption chiller (cooling conversion equipment)
- Absorber : Absorbent (lithium bromide solution)
- Heat production equipment : Hot water for district heating
Cold water supply system
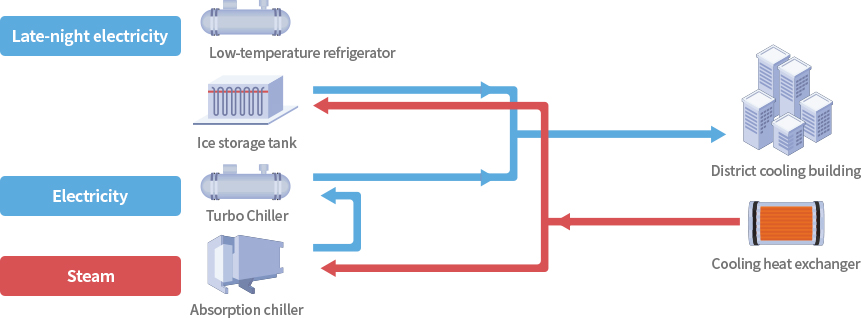
- Late-night electricity
- Low-temperature refrigerator
-
- Cooling heat exchanger
- Ice storage tank
- District cooling building
- Electricity
-
- Absorption chiller
- Turbo Chiller
- District cooling building
- Steam
-
- Cooling heat exchanger
- Absorption chiller
- Turbo Chiller
- District cooling building


